Objective:
Let us put Initiating a Project into context and look at what it really does for the project. The Starting up a Project process checks if the project is viable, while Initiating a Project is about building a correct foundation for the project so that all stakeholders are clear on what the project will achieve.
The alternative would be to allow projects to start after the Starting Up a Project process without knowing any of the following: planning, milestones, cost and level of quality. It is a bit like building a house on little or no foundation.
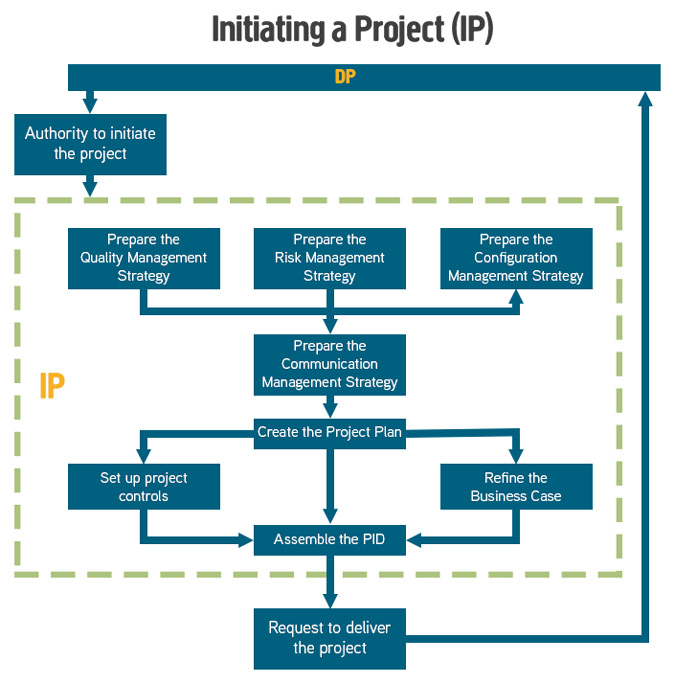
Initiating a Project can be a big investment for a company but it’s a necessary investment to plan and run the rest of the project. During Initiating a Project, the Project Manager will be creating a collection of management products to show: how the project will be managed, the cost, how quality will be checked, planned, how communication will be done, etc.
Project Initiation Document (PID):
Project Brief – Updated
The Project Brief comes from the SU process. The information in the Project Brief is expanded and refined and it will become part of the Project Initiation Documentation. Including the Business Case, which is completed here and the responsibility of the Executive and provides the information to justify the project. The Project Manager will most likely assist the Executive (part of PID). The Project Initiation Documentation forms a contract between the Project Manager and the Project Board.
Tailoring Prince 2
The Project Initiation Documentation should describe how the PRINCE2 method is tailored for that particular project. A PRINCE2 project should be tailored to suit the project’s size, environment, complexity, importance, capability and risk. If your project is a small one, such as to host a workshop with 10 people, or a very large one, like building a nuclear power plant, then you should tailor PRINCE2 to suit the project, as PRINCE2 can be applied to any type of project. PRINCE2 is designed to support all types of project, which makes it a little too complicated to simple projects. Therefore, you need to simplify it in your tailoring process, when you want to use it in simple projects.
Quality Management Approach
A Quality Management Approach describes how quality will be managed during the project. This includes the specific processes, procedures, techniques, standards, and responsibilities to be applied. A template is usually provided by the organization and only needs minor changes. This document is created at the initiation stage with the other approach documents and becomes part of the project initiation documentation. The Quality Management Approach also defines the various responsibilities for achieving the required quality levels, during the project.Preparing the Quality Management Approach , which will answer the question on how to ensure quality.
Quality Register
A diary of the quality events that take place during the project, such as workshops, reviews, testing, and acceptance. At first, the quality register will be empty and the project manager will get most data from the plans and product descriptions.
Risk Management Approach
PRINCE2 recommends that each project have its own Risk Management Approach document. This document defines the project procedures for risk management in terms of how risk will be identified, assessed, controlled, and communicated in the project. Another way to say this is: The risk management approach describes the specific risk management techniques and standards to be applied during the project, and the responsibilities to provide a good and consistent risk management procedure.Preparing the Risk Management Approach , which will answer how to manage risk during the project (that is, how to manage the rules of engagement for risk).
Risk Register
The Risk Register captures and maintains the information (both threats and opportunities) on almost all the risks that were identified and relate to the project. So it provides a record of risks, including their status and history. It is used to capture and maintain information on all the identified threats and opportunities relating to the project.
Change Control Approach
A Change Control Approach is used as a guideline to identify how, and by whom, the project’s products will be controlled and protected during the project. This includes both change and issue management. Preparing the Change Control Approach , which will give information on how to manage the products produced during the project.
Issue Register
The Issue Register captures and keeps track of all formal issues. It is regularly monitored by the Project Manager throughout the project. Just imagine a spreadsheet where each line is an issue and there are columns for Issue ID, Issue Type, Date Raised, Raised by, Description, Current Status, and Close Date. So, we can that the purpose of the Issue Register is to capture and maintain information on all the formal issues.
Communication Management Approach
The Communication Management Approach is one of the four approach (guideline) documents created at the start of the project by the project manager and is then used by the project manager as a guideline on how to communicate with stakeholders (both internal and external to the project) during the project. So this document contains such information as: the different types of stakeholder in the project, whether they support or oppose the project, the type (format) of information to communicate, when and how often to communicate, etc. In other words the Communication Management Approach facilitates engagement with stakeholders through the establishment of a controlled and bi-directional flow of information.Preparing the Communication Management Approach , which will answer questions related to communication with stakeholders.
Setup of Project Controls, which will provide information on how the Project Board can control the project.
Project Plan
The Project Plan for the whole project is created Initiation Stage. The Project Plan is a plan for the whole project created which includes all Product Descriptions (part of PID). The Project Product Description (PPD) is created in the Starting up a Project process and is part of the Project Brief It is then refined during the Initiating a Project process when creating the Project Plan, so it is still used during the project. The Project Product Description is normally a 1-3 page description of the main product that will be produced by the project. The structure of this document is covered in both the quality and plans themes. The Project Manager will extract this information from the Senior User role which can be one or more people and will also involve subject matter experts who give feedback on what is and what is not possible to do.
Control Plan
An overview of how the project will be controlled (part of PID). Project controls document clearly shows how the project will be controlled and who will administer each control. Clear project objectives for the six project variables (time, cost, quality, scope, benefit and risks).
Benefits Management Approach
The purpose of the Benefits Management Approach is to identify the benefits and most importantly, to select how the benefits can be measured so that it is possible to show that they have been reached. You can then compare the new results to the current situation as it is today or at the start of the project (baselined measurements).The Benefits Management Approach is an overview of what and when Benefits will be realized both during and after the project, and who (Senior User) is responsible for these benefits.
Request to deliver a project:
The final output of the Initiating a Project process is a request to the Project Board to deliver the project or, in other words, to sign off on the PID and allow the project to continue.